The History of Neurofeedback: Part I
How does Neurofeedback work? Why is it so effective in treating brain conditions as varied as ADHD, traumatic brain injury, seizures and learning disabilities? And so on. In the interest of answering these and other questions, we thought we’d start with the history of this remarkable, non-medicinal treatment for the brain known as Neurotherapy now available in Chicago.
Learn More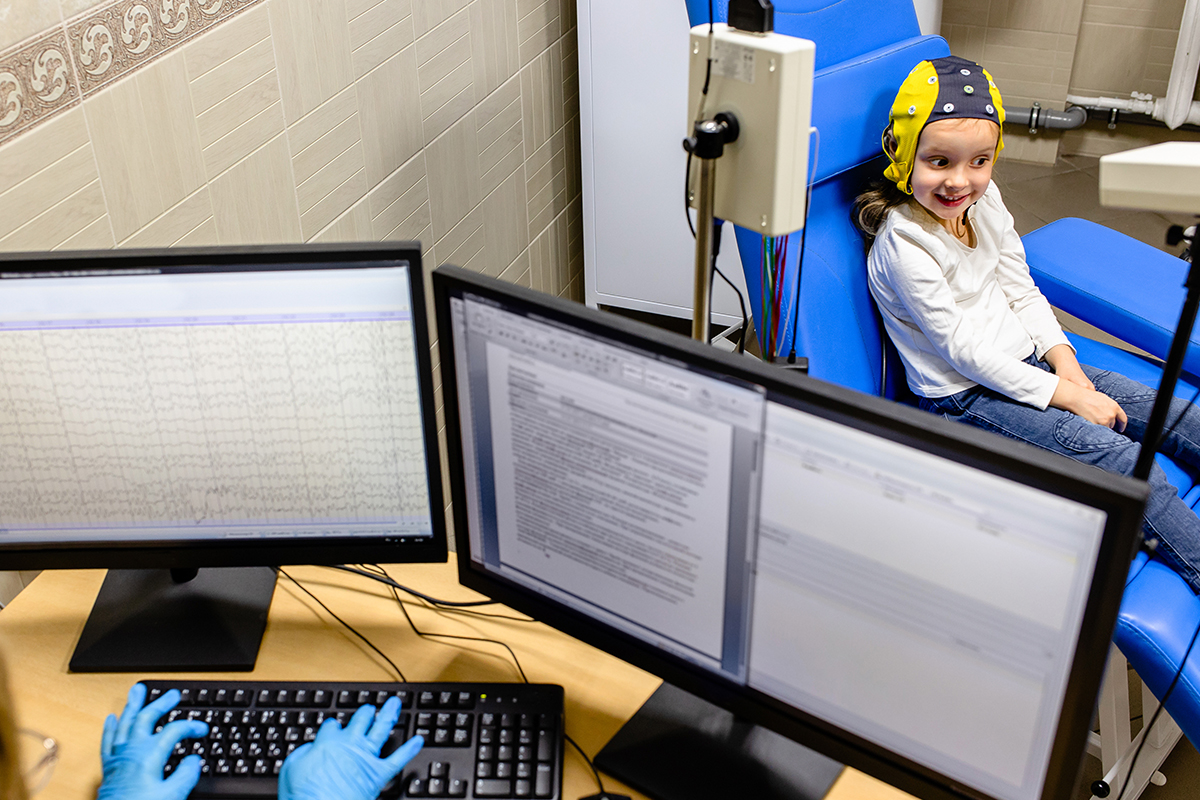
Neurofeedback: Science or Shamanistic Ritual?
Neurofeedback: Science or Shamanistic Ritual?
By Ari Goldstein, Ph.D.
The human brain is a fascinating organ that constantly seeks to improve itself. The capacity of the brain to grow and develop in response to environmental stimuli is magnificent. From trepanation to phrenology, behaviorism to psychoanalysis, man has sought to better understand this splendid organ. As we begin the 21st century, our knowledge of the brain continues to grow and develop at a rapid pace. Technology allows us to understand and improve how the brain functions in manners never before thought to be possible. One of the ways current science allows us to understand how the brain functions is through analysis and normalization of the electrical patterns created by the brain. The process of reading and analyzing the brain’s electrical patterns is known as a Quantitative EEG. The data provided through this process helps individuals and their clinicians understand how their brain is functioning and processing information, thereby allowing for much more targeted clinical interventions.
When I was a psychology student in College, we were taught that the brain does not grow much in adulthood. As the understanding of the brain and neuronal functioning has increased, we now know that the brain is highly capable of adapting and growing even into old age if given the right stimulus. The process of EEG Neurofeedback involves teaching the brain to grow and develop more efficient patterns of functioning. Through a series of games and activities played while connecting their brain to the computer, individuals learn to better self-regulate and improve the efficiency of their brain function.
I was first introduced to EEG Neurofeedback by Dr. Sam Effarah, and my thinking around learning and the brain changed dramatically. I was able to very clearly see quantitative data on how the brain was functioning, and saw how we could gain an amazing amount of very functional and actionable knowledge from a Quantitative EEG assessment. I also began to see the tremendous value in teaching people to regulate their own functioning through neurofeedback in a much more meaningful and lasting way. Clinicians could very clearly see patterns in the brains of individuals diagnosed with ADD/ADHD, learning disabilities, anxiety, depression, and autistic spectrum disorders that were different from the average brain. Often times, the frontal lobe of the brain in individuals with attention difficulties has far too much of the slow wave known as “Theta”. This can cause a state of cognition known in scientific terms as “La La Land”. A fast spindly wave known as “High-Beta” was often seen throughout the brain of those with hyperactivity and anxiety. Disconnections between areas of the brain that process auditory and visual stimulus often become apparent through the Quantitative EEG in those diagnosed with learning disabilities.
When we began using EEG data to drive some of the work we do at Cognitive Solutions, the level of skepticism among our colleagues and patients was high. It was almost as if we were practicing some form of shamanistic ritual to help people. As time went on, more and more people began to try it out. We had patients referred to us with a range of symptoms, including attention disorders, learning disabilities, anxiety, depression, and autism spectrum disorders. Most patients reported improvement in a range of symptoms after completing only a few sessions. Some took more time to see improvement, but those who stuck with it generally reported significant improvement in their functioning over time.
The research on Neurofeedback is strong (isnr.org). While detractors would note the lack of double blind studies, a host of solid research studies into neurofeedback show quantifiable evidence of improvement for a range of brain based dysfunctions. Anecdotal cases can be found all over the world for individuals who have seen improvement for a range of symptoms affecting their daily functioning. The American Psychological Association has consistently given higher and higher efficacy marks to this treatment as more and more solid research has been conducted.
At Cognitive Solutions Learning Center in Chicago, we have worked with thousands of patients using neurofeedback over the past fifteen years. Most have seen tremendous benefits in quality of life as a result of this treatment. As I have watched the science catch up to what I have seen personally in our clinic, I am glad to have discovered this amazing intervention tool. From shamanistic ritual to true science, it appears that neurofeedback is a viable and drug free option for many patients to treat a range of brain based symptoms.
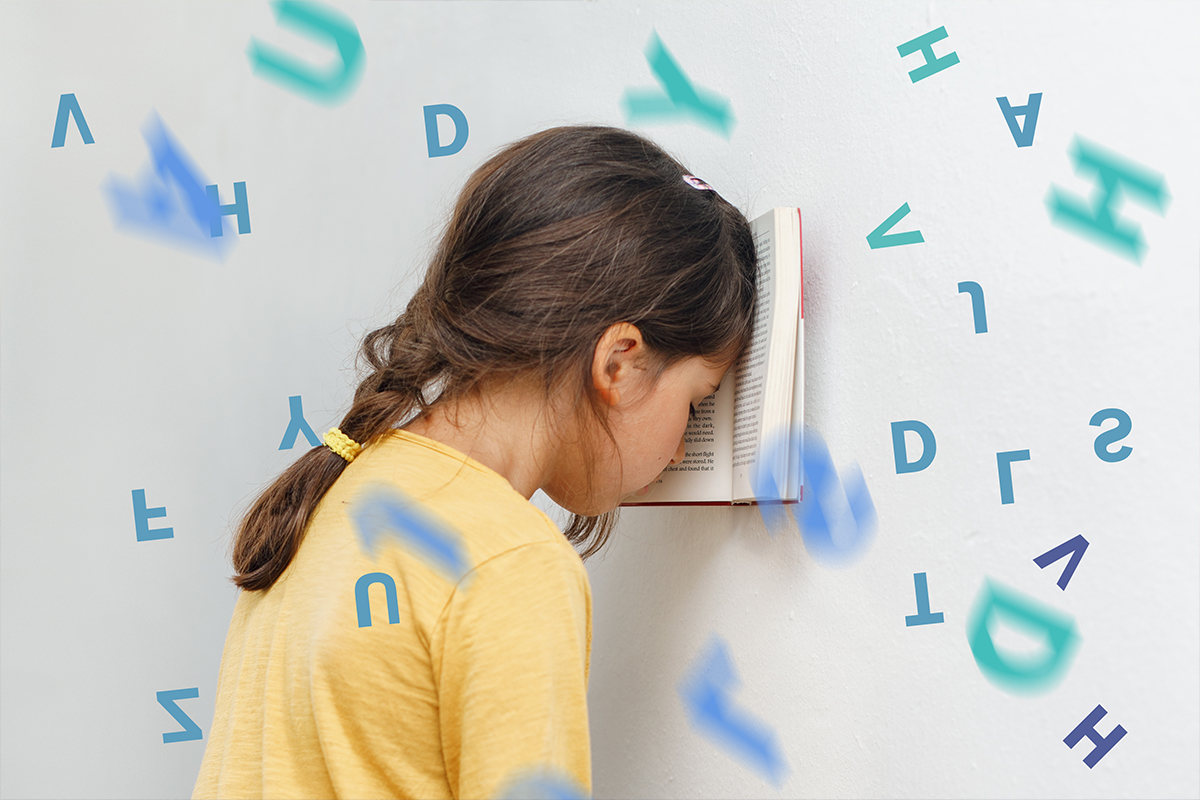

Neurofeedback For Dyslexia
EEG Neurofeedback For Dyslexia
Our previous blog discussed adult dyslexia, its symptoms, and how the proper testing and diagnosis is important for treatment planning. Along with the proper testing and diagnosis for a learning disability such as dyslexia, certain treatments are available that can improve brain function in a meaningful way.
Neurofeedback training or EEG Neurotherapy targets the symptoms of dyslexia at their foundation – the brain! Often visual, auditory, and/or executive processing deficiencies are present in those with learning disabilities, and neurofeedback directly targets these areas of brain function. Not only can it target the primary symptoms, but also the secondary symptoms of learning disabilities including social emotional and self esteem difficulties. Neurofeedback produces long-term changes in an individual’s functioning and mental health.
There is a great deal of research that supports EEG neurofeedback training for those with learning disabilities, cognitive deficits, and emotional dysfunction. In addition to this research, there is support for treating symptoms and deficits that are specifically related to dyslexia with neurofeedback. By examining various regions of the brain through brain imaging, including QEEGs (brainmaps), researchers have found that structural differences in the left side of the brain are present in those with Dyslexia and can be treated with neurotherapy. This makes sense given that the left side of the brain is primarily involved in the representation and comprehension of language. Breteler (2010) conducted research examining the improvements in children with dyslexia and specifically looked at reading and spelling. They were able to find a significant improvement in spelling for the children that received the neurofeedback training when compared to the control group that did not receive the neurofeedback training. Also, their findings suggest that improvement in attentional processes in the brain could be partially what is contributing to the spelling improvements (Breteler, 2010).
Attention difficulties (ADD/ADHD) are common for those of all ages with various learning disabilities. Hundreds of individuals with these diagnoses and more have seen improvements with neurofeedback training at Cognitive Solutions Learning Center in Chicago. Neurofeedback training has shown a high level of clinical success around the world, and is supported by a strong base of research in neuroscience. There is a solution to help individuals with brain based disabilities like dyslexia make changes to their brain that have a lasting impact, no matter their age.
Read more about The Cognitive Solutions Learning Center approach to Neurofeedback for Dyslexia Here
If you feel you or your child may suffer from dyslexia contact Cognitive Solutions Learning Center in Chicago at (773)755-1775, or visit us online at www.helpforld.com, to find out more about our programs.
*Breteler, M. (2010). Improvements in Spelling after QEEG-based Neurofeedback in Dyslexia: A Randomized Controlled Treatment Study. Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback, 35(1), 5-11.
Learn More